As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.
















Biodiversity and Food Security: Two pieces of the same puzzle
India is highly dependent on the agriculture sector for its food security, and biodiversity loss leaves crops vulnerable to pests and diseases, thereby lowering yields. It also leads to the increased occurrence of invasive species and reduces the pollinator population. Thus, the interlinkage between food security and biodiversity loss needs to be understood in its entirety.
Innovating for a Better Future!
A brainchild of Professor Flemming Besenbacher, Professor of Nanophysics at Aarhus University, Denmark, UNLEASH is a global initiative that aims to bring together the next generation of youth from across the globe, providing a platform to share ideas, build networks, and create innovative and scalable solutions to progress towards the SDGs. It has been hosting the Global Innovation Labs annually, with the previous editions being in Denmark (2017), Singapore (2018), and China (2019).
Carbon Tunnel Vision Dominates the Climate Crisis Narrative
- The climate crisis is embedded in a breakdown of the larger socio-ecological system, wherein solving carbon will not necessarily solve the crises we are in.
- The West has been pushing a carbon-obsessed mitigation narrative.
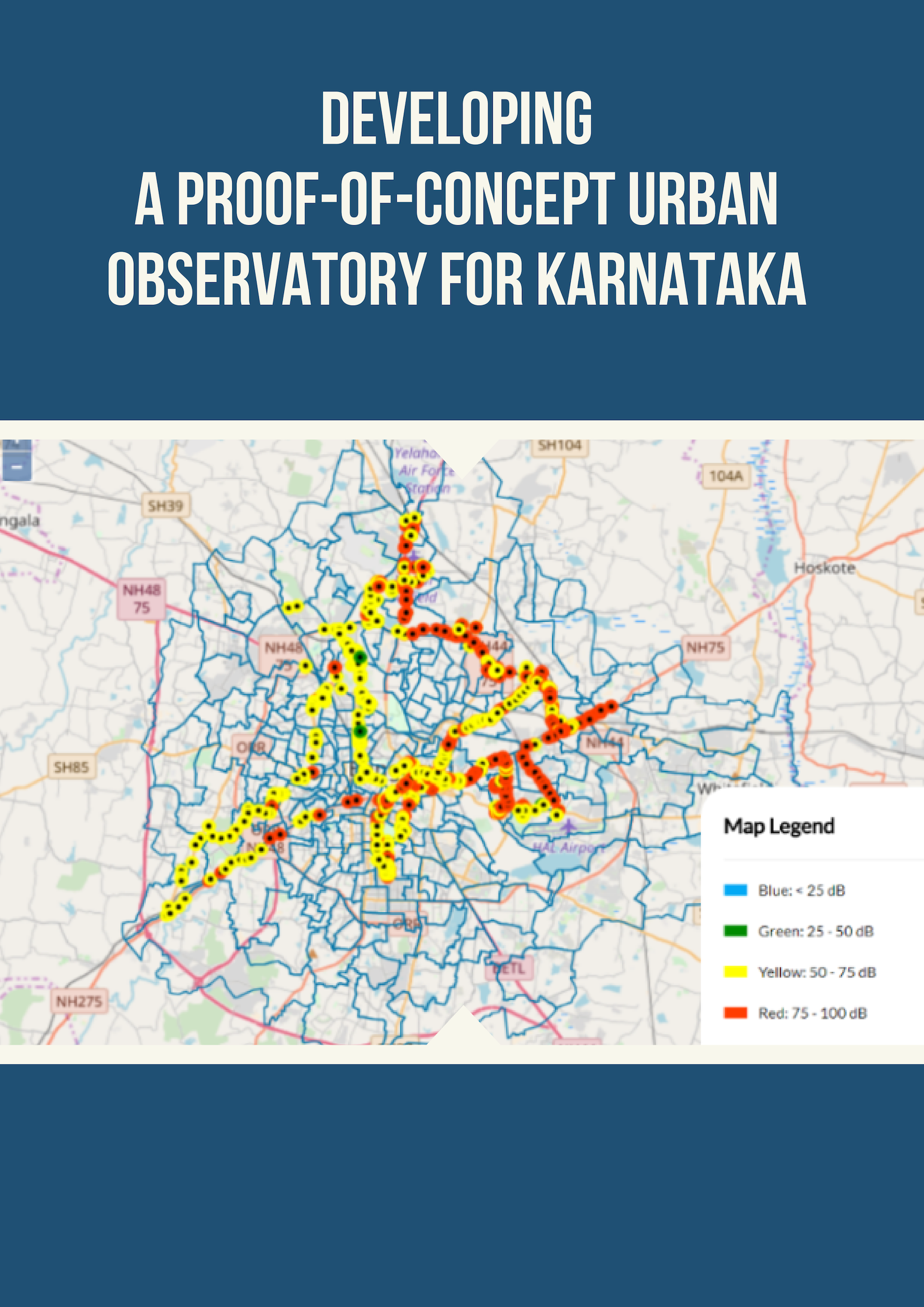
Could digital twin models help combat water shortage in India?
There is little doubt that India’s water shortage problem is real and happening! Numbers confirm the alarming reality. According to the Ministry of Jal Shakti, India’s annual average per capita water availability was assessed at 1816 cubic metres and 1545 cubic metres in 2001 and 2011, respectively. This could further reduce to 1367 cubic metres in 2031. In 2019, NITI Aayog reported that nearly 600 million Indians are water-deprived and about 40% of the population will not have access to drinking water by 2030.
Climate atlas of India: District-level analysis of historical and projected climate change scenarios
Climate change is the biggest challenge today and will be so in the coming decades. The increase in extreme events and their impact on natural and artificial ecosystems and lives and livelihoods are conspicuous. Formulation of climate policies and planning and implementation of programmes and projects for adaptation require climate information at various spatial scales.
Opinion: Climate adaptation must be transformational, not just fighting fires
For adaptation measures to work efficiently, assessments of capacity, technology and financial needs should be integrated. Regional (national and sub-national) stocktakes should now be initiated to move forward with the Global Goal on Adaptation.
It’s Time to Feed Our Soil
Soil — the second-largest natural carbon sink after oceans — has an enormous capacity to capture atmospheric carbon dioxide.
When functioning with loads of microorganisms, adequate water, air, minerals, and organic matter, soils are very much alive and healthy, sustaining ecosystems.
No Silver Bullet: Considerations for India’s Net-Zero Strategy
CSTEP's latest report No Silver Bullet: Essays on India’s Net-Zero Transition throws up some pertinent questions on India's net-zero strategy. CSTEP organised a virtual event on 15 December 2022 to discuss the questions and considerations brought up by the report. For more details, please refer to the concept note and agenda.
Revenue recycling: How governments can address carbon pricing trade-offs
While carbon taxes can disproportionately hurt the poor, governments can plough back some of this revenue to mitigate inequities, while incentivising low-carbon technological alternatives.
Towards a Policy Framework for Financing Future Loss and Damage
The inclusion of loss and damage (L&D) to the COP27 agenda is a positive first step in achieving climate justice. While vulnerable nations have been fighting for its inclusion into global discourses for decades, the recent climate-induced disasters across the world, especially in Pakistan, have played a pivotal role in its induction.
