As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.








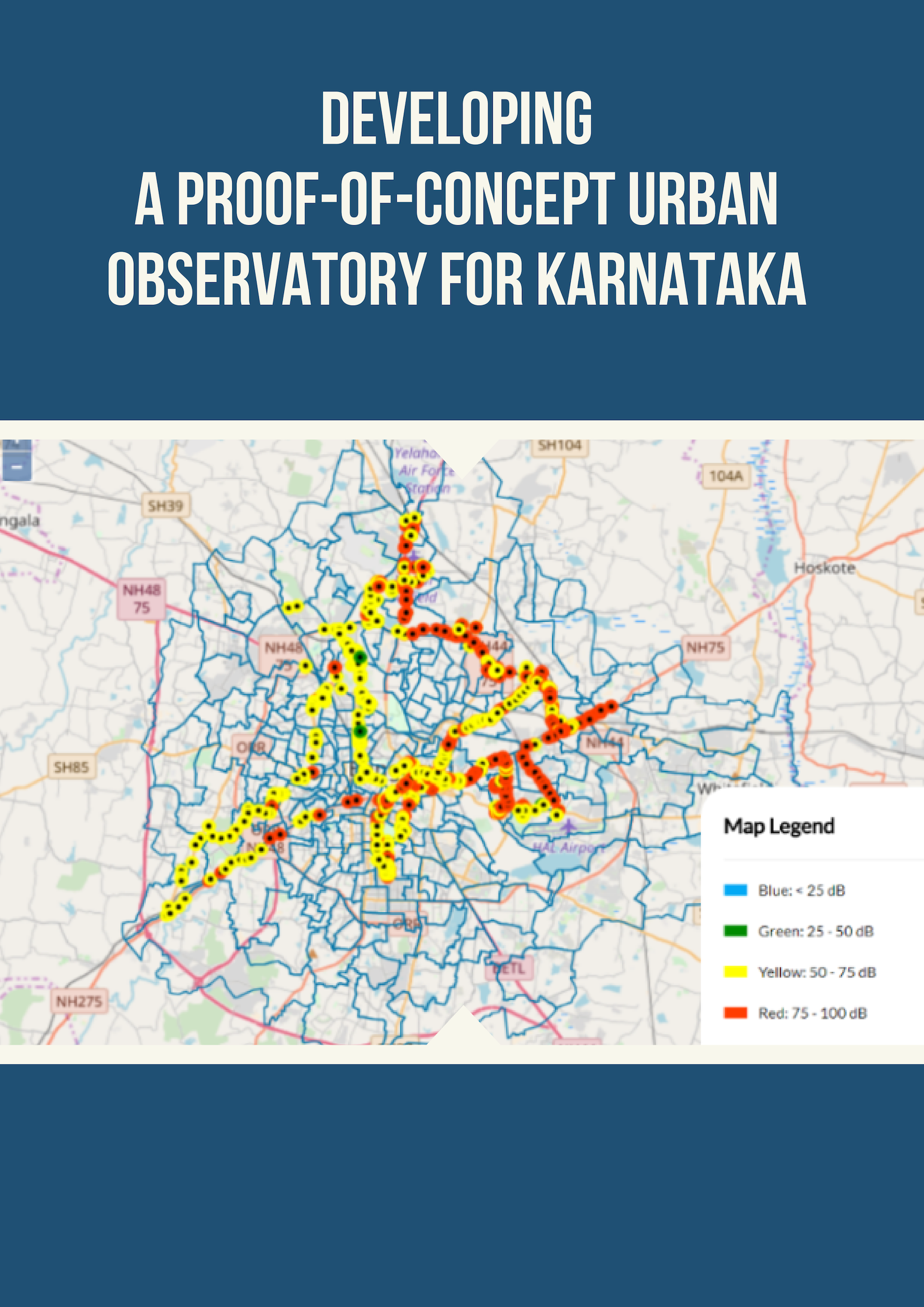








Integrated Urban Sanitation Decision Support Tool
Integrated Urban Sanitation Decision Support Tool
Study of the potential for deepening the coverage of Perform Achieve and Trade (PAT)
The study is an attempt to identify if more industrial manufacturing units could be added to the existing list of sectors leading to PAT 'deepening'. This study aimed to explore the possibility of deepening the scope of energy savings by introducing more industrial units into PAT from within the existing cement, fertilizer, iron and steel, textile, pulp and paper and Chlor-Alkali sectors. It concludes that there are a large number of small-scale units which do not fall under the PAT criteria of notifying as DC.
Climate Change Vulnerability and Adaptation in South Asia
Climate Change Vulnerability and Adaptation in South Asia.
Benefit Cost Analysis of Emission Standards for Coal-based Thermal Power Plants in India
In December 2015, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change notified emission standards for limiting sulphur oxides, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter and mercury emissions in coal-based thermal power plants. As of December 2017 (the deadline for meeting these standards), compliance was poor. Further, other government departments under the Ministry of Power (MoP) are mulling over a delay in implementation of these standards. In this context, this study evaluated the benefits and costs associated with the implementation of these emission standards.
Quality of Life for All: A Sustainable Development Framework for India's Climate Policy (Interim Report)
A Sustainable Development Framework for India's Climate Policy (Interim Report).
A Study of Energy Efficiency in the Indian Iron and Steel Industry
A Study of Energy Efficiency in the Indian Iron and Steel Industry
Technology Options for Faecal Sludge Management in Developing Countries: Benefits and Revenue from Reuse
This article provides technology options for the treatment of Faecal Sludge (FS) in developing countries to minimise exposure to FS and assesses its benefits along with possible revenue generation from reuse. FS that is collected from septic tanks poses management challenges in urban areas of developing countries. Currently, FS is dumped into the urban and peri-urban environment, posing great risks to the soil, surface water and groundwater quality.
Taking lessons from refugees in Europe to prepare for climate migrants and exiles
With millions of refugees pouring into countries in Europe, renewed attention is being paid to those who are displaced. This article combines some of the current lessons learned from Europe with previous studies on migration related to climate change and provides recommendations to be included in policy. Preparation in advance, regional agreements, and mechanisms for better integration of those who are displaced are highlighted.
Quality of life for all: A sustainable development framework for India's climate policy
This study placed improving quality of life at the centre of India's national climate policy and asked what happens to greenhouse gas emissions with such an approach. Using bottom-up scenario analyses, the sectoral interventions modelled in this research demonstrate that it is possible to get close to achieving the country's climate targets while improving quality of life at the same time.
Oxygen stability study of Li-rich compound: First Principle Analysis
High energy density Li-rich layered cathode materials suffer from structural instability at high voltage. It is known that oxygen stability influence the structural stability of Li2MO3 (M=Co/Mn/Ni). Oxygen stability with partial de-lithiation has not been clarified in presence of multiple d-orbital elements. This work presents density functional theory based study of Li1.17Ni0.17Mn0.67O2. In the series of Li-rich compounds, end point material is Li2MnO3, in which oxidation of Mn4+ compensates with oxidation of O2- to O2 while charging.
