Energy is a key factor in combating climate change, one of the biggest challenges the world is facing today. India has committed to cutting emissions to net zero by 2070 and set ambitious targets for adopting renewable energy. Achieving these targets requires careful planning and an overhaul of our current energy system.
Our work aims at enabling policies that encourage the adoption of rooftop solar, facilitate the development of technology for energy storage, strengthen the grid and transmission infrastructure, advance hydrogen technologies, and promote green mobility. CSTEP's research looks at the various aspects of mainstreaming renewable energy for a cleaner, greener energy sector.











Continued Support for the Implementation of UDAY Initiatives in Karnataka
An important concern with distribution companies (DISCOMs) is the wide gap between the costs incurred and the revenue realised by them. CSTEP proposes to carve out an implementation plan to improve the actual revenue realised for the energy supplied by focusing on three areas:
SERIIUS
Solar Energy Research Institute for India and the United States (SERIIUS) is a joint research consortium for clean energy research. It was announced under the flagship programme Partnership to Advance Clean Energy (PACE) by former US President Barack Obama and former Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh, in November 2009. The Department of Energy (DOE, US) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST, Govt.
End-use Energy Efficiency: A Path for Decarbonisation
In light of India's Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) commitments, we conducted an analysis to understand the contribution of energy efficiency to India's climate targets. This policy brief provides insights into the role of energy efficiency in reducing India's emissions. The study found that in order to achieve the NDC pledge, ongoing efforts in energy efficiency (along with efforts in alternate fuels and renewables) need to be rigorously implemented at the sub-national level as well.
Energy-Efficient Irrigation Pumps
The study assessed the feasibility of replacing 5 lakh inefficient irrigation pumpsets (IPs) with energy-efficient IP sets across five Electricity Supply Companies (ESCOMs) in Karnataka. Pilot studies revealed that the efficiency of existing IP sets was less than 30%. The efficiency of current energy-efficient IP sets range from 35%-55%, providing huge potential for energy-savings on replacement. By replacing 5 lakh IP sets, GoK could save about INR 900 crore from subsidy outlays every year.
Karnataka's Energy Mix: Computational Model for Energy Planning
The Government of India has ambitious targets of achieving 175 GW of renewable energy by 2022. As of March 2017, Karnataka's renewable energy capacity share stood at around 35% (out of 20 GW of the installed generation capacity mix). This is expected to increase as the state (KREDL) aims to have 6.86 GW of solar and 4.9 GW of wind generation capacity by FY19.
Feasibility of Supplying Dedicated Agricultural Feeders with Solar Power in Karnataka
The agricultural sector in Karnataka accounts for 39% of the state’s electricity (~21,344 MU). This is provided for free, or at heavily subsidised rates, to farmers. Moreover, electricity is not metered. This has led to an estimated revenue loss of INR 9,295 crore for state DISCOMs. The Government has attempted several initiatives to reduce this loss, one of them being segregation of domestic and agricultural feeders.
Studies for the Government of Karnataka
1. Sustainable Urban Planning Strategies for Cities in Karnataka
Techno-Economic Analysis of Stand-Alone Solar PV and Battery-Based Micro-Grids in Karnataka
This project was a part of the Indo-US collaborative research platform Solar Energy Research Institute for India and the United States (SERIIUS; www.seriius.org) and was funded by the WIPRO Foundation.
Strategic Roadmap for Implementation of UDAY Scheme
CSTEP studied the implementation of the Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY) in Karnataka. UDAY, launched by the Government of India in 2015, aims to improve the financial health of state-owned power distribution companies (DISCOMs). Based on the study findings, CSTEP recommended measures for effective implementation of the scheme in order to meet its objective of reducing losses among DISCOMs and increasing operational efficiency.
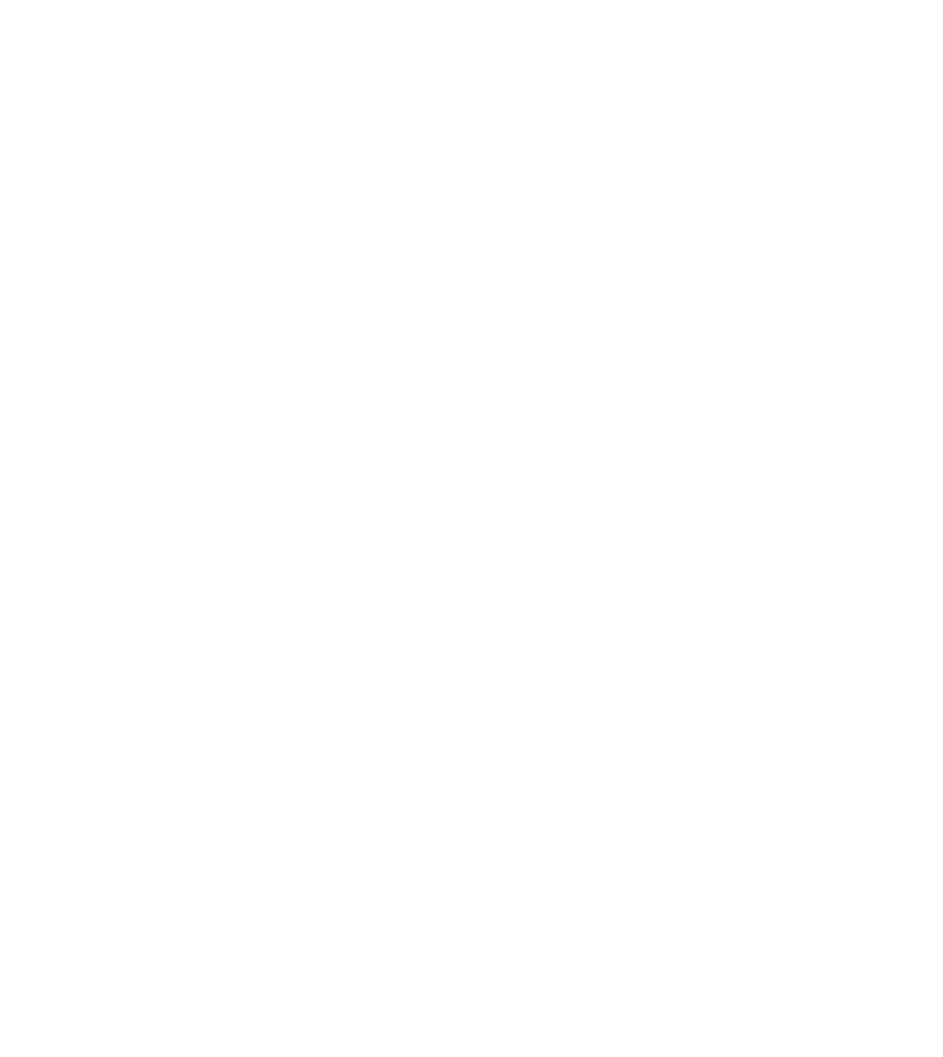
RE potential estimation in Lakshadweep
CSTEP worked with the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) to develop RE (floating solar/RTPV/wind) + battery storage system designs for 12 islands in Lakshwadeep. The project aimed to replace 60% diesel-based consumption in these islands. CSTEP researchers visited the islands for site surveys and feasibility assessment of RE installations.