As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.
















Too hot to handle?
March 2023 was the second-warmest March for the world in the last 174 years, says the March 2023 Global Climate Report by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). With the seventh-warmest January and fourth-warmest February (in the last 174 years) also being this year — as reported by NOAA — 2023 has, indeed, had a warm start. So, are warmer years becoming a reality?
India’s Building Code Has a Blind Spot for a Whole Category of Emissions
Building codes are not new to India, and the first iteration of the National Building Code (NBC) dates back to 1970. While the NBC had general building guidelines in place, there were none pertaining to regulating emissions from the building sector. In 2002, the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) was established under the Energy Conservation Act to spearhead energy and emission-related regulations.
Climate Action Has to Shift from Being Reactionary to Precautionary
We are in a state of climate emergency. The past year was witness to some of the worst floods in Pakistan, extreme heatwaves in the United Kingdom, and devastating hurricanes in the United States. Climate disasters became the norm in India, too, during the first seven months of 2022 as 241 out of 273 days were marked by an extreme weather event — cold waves, heatwaves, cyclones, thunderstorms, torrential rains, floods, landslides, droughts, dust storms, hail, or snowstorms — according to a study by the Centre for Science and Environment.
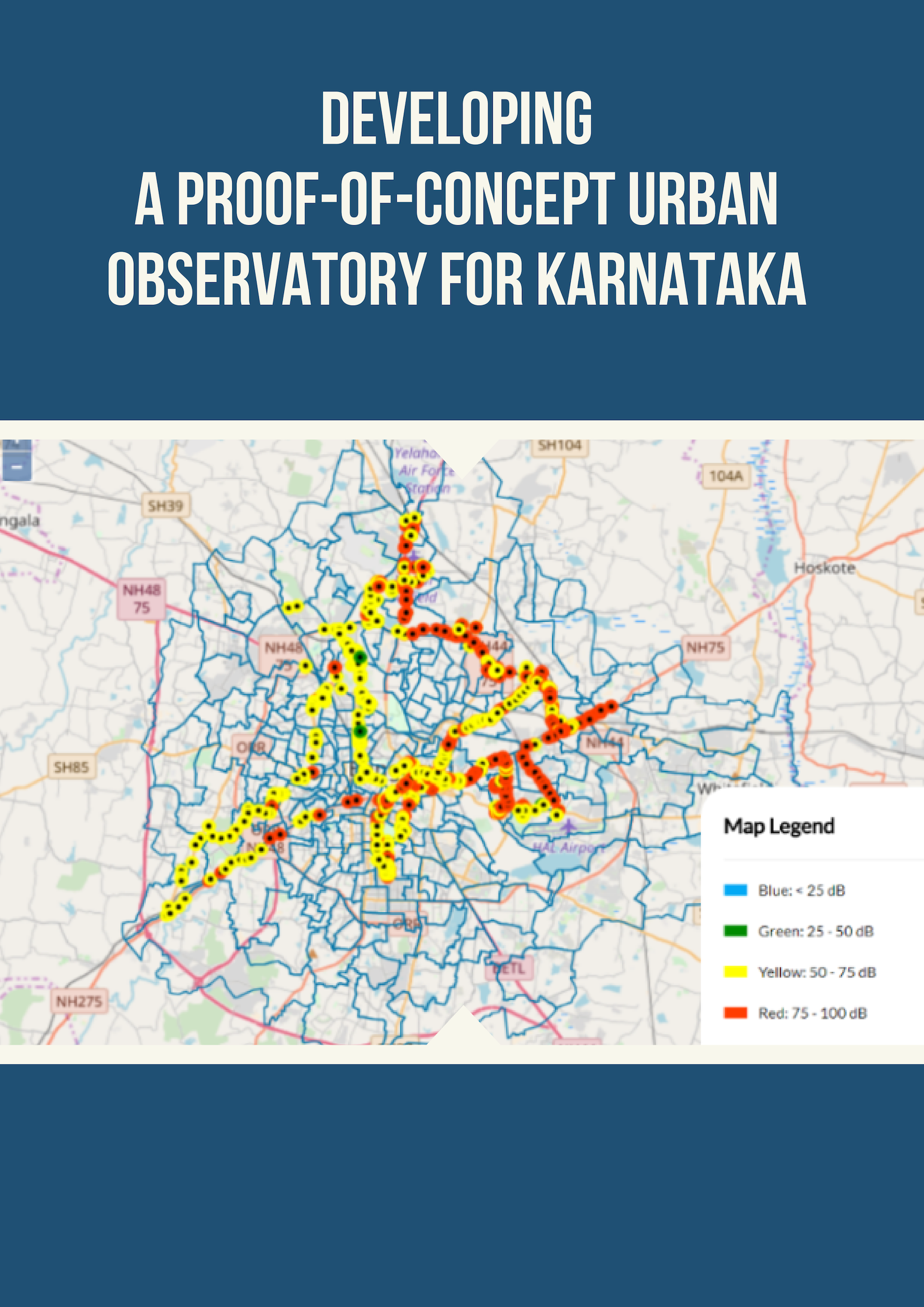
PRESS RELEASE: Bengaluru has the potential to reduce PM10 emissions by 21% by 2024, says CSTEP study
The studies, “Emission Inventory and Pollution Reduction Strategies for Bengaluru” and “Identification of Polluting Sources for Bengaluru: Source Apportionment Study”, point to transportation and road dust as the biggest contributors to air pollution in Bengaluru city. These studies were conducted under the aegis of KSPCB and supported by The Bloomberg Philanthropies and Shakti Foundation, to generate scientific data and contribute to India’s National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
PRESS RELEASE - CSTEP Study: Prepare for Warmer Temperature and High-Intensity Rainfall Events in Eastern India
A study by the Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP)—a Bangalore-based think tank—on the climate of eastern India underscores the need for climate risk mapping and climate action. The study ‘District-Level Changes in Climate: Historical Climate and Climate Change Projections for the Eastern States of India’ projects changes in temperature and rainfall patterns in Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal—the eastern states of India—over the next three decades compared to the historical period (1990–2019).
PRESS RELEASE: Report Launch: Satellite-Based Mapping and the Quantification of PM2.5 in India
The Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP) used satellite-based products to study the spatial patterns, hotspot areas, and rural–urban contrasts in PM2.5 in the Delhi-NCR, Kanpur, and Bengaluru regions for the calendar year 2019. Titled ‘Satellite-Based Mapping and the Quantification of PM2.5 in India,’ the official report was launched during a virtual event held on 28 February 2022. Three policy briefs based on the satellite-based mapping of Delhi-NCR, Kanpur, and Bengaluru were also released along with the report.
PRESS RELEASE: CSTEP Study: High-Intensity Rainfall Events Expected in North-Eastern India
The Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP)—a Bengaluru-based think tank—published a study on the climate of north-eastern India titled ‘District-Level Changes in Climate: Historical Climate and Climate Change Projections for the North-Eastern States of India’. The study projects changes in temperature and rainfall patterns in Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura over the next three decades (2021–2050) compared to the historical period (1990–2019).
PRESS RELEASE: CSTEP Study: Winter Minimum Temperatures Expected to Be High in Northern India
The Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP)—a Bengaluru-based think tank—published a study on the climate of northern India titled ‘District-Level Changes in Climate: Historical Climate and Climate Change Projections for the Northern States of India’. The study projects changes in temperature and rainfall patterns in Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh over the next three decades compared to the historical period (1990–2019). It analyses two representative scenarios: moderate emissions (RCP 4.5) and high emissions (RCP 8.5).
PRESS RELEASE: New report asks important questions as India develops net-zero strategy
As we inch closer to another global climate summit, COP27, climate projection models will once again be thrust into the limelight as they play an important role in devising net-zero strategies. However, assumptions and estimates for India’s ‘net zero by 2070’ target need to be reviewed carefully given the deep uncertainties involved. There is no correct pathway to net-zero emissions.
PRESS RELEASE: CSTEP Report Predicts a Warmer and Wetter Future for India
The Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP)—a Bengaluru-based think tank—has published the Climate Atlas of India: District-Level Analysis of Historical and Projected Climate Change Scenarios. The report summarises the findings from CSTEP’s historical climate analysis and future climate projections at a district level for the 28 states of India (excluding union territories), published as regional reports in 2022.
