As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.
















Energy and Emissions Implications for a Desired Quality of Life in India Part 2: Demand Estimation
This project aims to understand the synergies and trade-offs involved in facing the unenviable challenge of balancing their developmental goals and climate targets.
Thorium-Utilisation Pathways for India
- For India, thorium-based nuclear power has been the endgame, and will form the final phase of the three-stage Indian nuclear programme for energy security developed by Dr Homi J. Bhabha in the 1950s. This report assesses strategies for thorium adoption in the Indian nuclear power sector.
Long-term energy system planning considering short-term operational constraints
-
Long-term planning models give an insight into possible energy scenarios and do not examine technologies in detail.
-
Renewable energy sources have spatial and temporal intermittency that causes challenges for short-term system operations.
-
Including operational details of generators directly in a planning model reduces intricacy of handling separate models.
-
Operational constraints increase usage of conventional generators and reduce overall capacity needs in planning model.
Mobility & Urban Poor
Policy should focus onthe disaggregated needs of the public system, integrating land use and transport.Improvements to Non-Motorized Transit facilities with emphasis on importance of pedestrians Improvements to the bus system includes pricing, timing and awareness of service quality Social impact studies (positive & negative) of major projects should be mandatory, inclusive and participatory.
Electronic Waste Management in India
An article on Electronic Waste Management in India published in the Annual Technical Volume, Environmental Engineering Division Board (Session 2015-2016)
Sustainability Analysis and Energy Footprint-Based Design in the Product Lifecycle
In this paper, we study the concept of energy efficiency and specific energy consumption (SEC) of manufacturing processes.
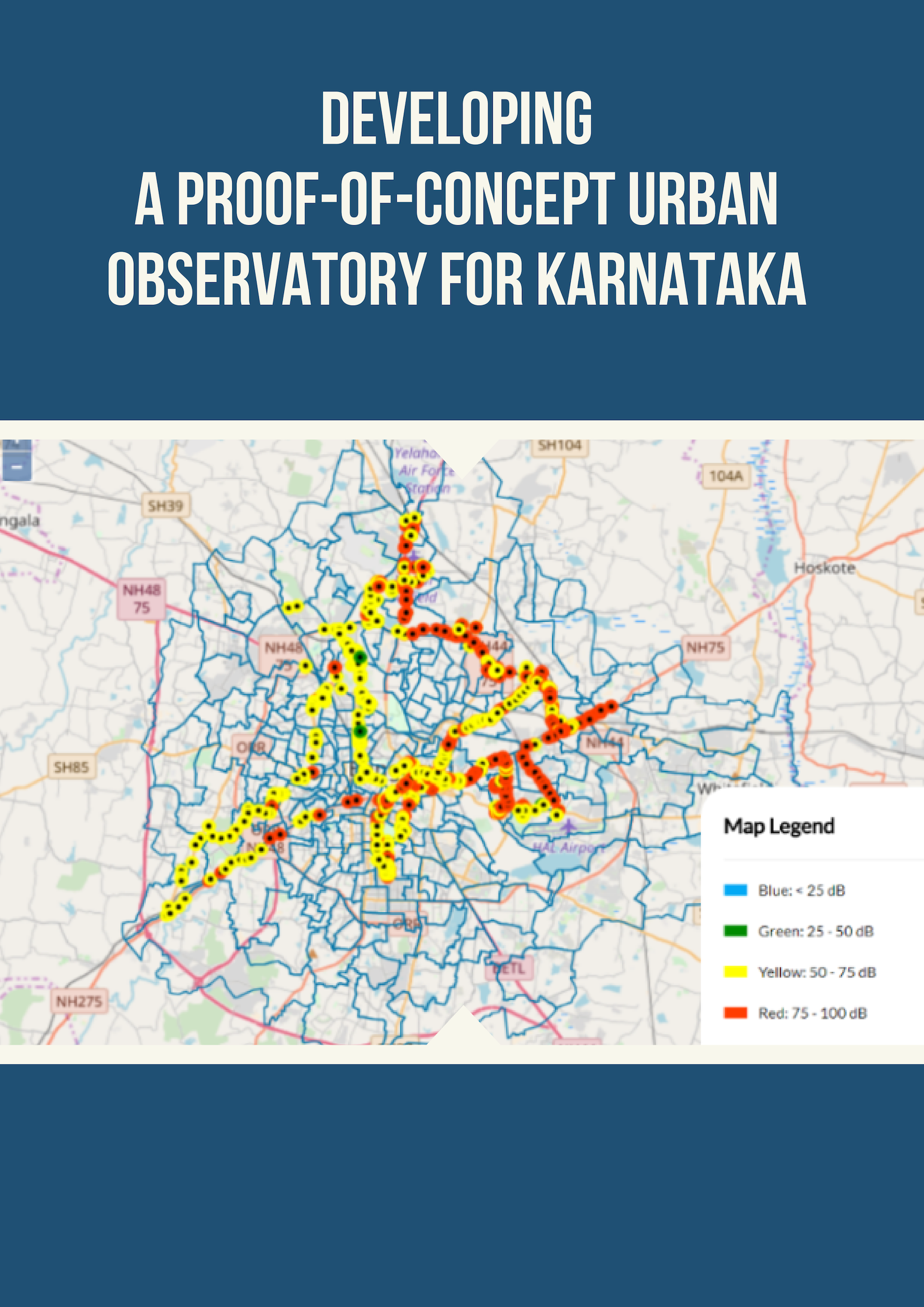
Platform for Integrated Sanitation Investment Planning (Proof of Concept): Review of decision support resources compendium
Effective decision-making support systems help decision makers in identifying, evaluating and choosing a technology that best suits context/conditions of a city/area/ward. In order to develop a tool which is of use to decision-makers, an evaluation of the existing support resources was considered necessary to identify challenges/gaps pertaining to content, design and usefulness of the resource in question.
CSTEP evaluated existing support resources for decision making, which include the following:
Karnataka: Greenhouse Gas Inventory
Anthropogenic emissions of carbon dioxide weighted by global warming potentials,
constitute by far, the largest part of the emissions of greenhouse gases. Of these carbon dioxide emissions, those that are produced from fuel combustion make up the great majority. The carbon dioxide emissions from burning biomass that a majority of rural households use for cooking is not considered, as biomass is considered to be carbon neutral.
Data Visualisation: On Think Tanks
Increasing urbanisation and per capita GDDP:
Karnataka is one of the most urbanised states in India; 39% of the state consists of urban areas whereas the national urban area average is 31%. Karnataka is expected to be 50% urbanised by 2026, and that would mean 33 million people to be accommodated
in the cities of Karnataka. Urbanisation and GDDP (Gross Domestic District Product) follow similar trends in growth. As the GDDP in the state has been growing, so has urbanisation. This relationship, however, also highlights the growing inter-regional disparity in economic
