As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.
















GHG Platform India
CSTEP is one of the project consortium partners and the lead sector partner for Energy Sector Emissions Estimates in the GHG Platform India project.The Platform is a collective civil-society initiative, established with an objective to provide independent estimation and analysis of India’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across key sectors such as energy, waste, industry, agriculture, livestock, forestry, and land-use and land-use change sectors.
Roadmap for Achieving India's NDC Pledge
CSTEP developed a roadmap to achieve India’s NDC target of reducing its emissions intensity by 33%-35% of 2005 levels, while meeting our developmental goals. We examined the emission intensity of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) (kgCO2e/INR) by its two constituents: emission intensity of energy (kgCO2e/kWh) and energy intensity of GDP (kWh/INR). The latter was evaluated in detail to assess the role of energy efficiency in end-use sectors.
Climate Change : Need to act now
The threat of climate change is a serious global concern. India faces the twin challenges of adaptation and mitigation. As a country with many critical sectors and regions that are highly climate sensitive, there are significant costs associated with addressing the impacts of climate variability and future climate change. The National Action on Climate Change has set up an Expert Group to evolve Low Carbon Strategies for Inclusive Growth.
A study of Energy Efficiency in the Indian Cement Industry
Under National Mission on Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE), Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) is one of the flagship programmes launched by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), Ministry of Power and Government of India to enhance the cost effectiveness of the improvements in Energy Efficiency (EE) in energy-intensive large industries (known as Designated Consumers or DCs). The identified cement DCs have a minimum annual energy consumption equivalent to 30,000 tonnes of oil equivalent (toe) or above.
The Final Report on Expert Group on Low Carbon Strategies for Inclusive Growth
On a per capita basis, India is one of the lowest emitters of greenhouse gases in the world, yet it is threatened by the impact of global warming and climate change. The Expert Group on Low Carbon Strategies for Inclusive Growth has evolved a macro-model to fully elucidate the inter-sectoral implications of different mitigation measures and ensure that the low carbon strategies being recommended are mutually consistent with each other. The model output is summarised through two endpoint scenarios: BIG (Baseline, Inclusive Growth) and LCIG (Low Carbon, Inclusive Growth).
A Sustainable Development Framework for India's Climate Policy
As a large developing country, India’s challenge is to meet its development aspirations in a carbon-constrained world. This study, undertaken by CSTEP, uses Sustainable Development (SD) as the overarching framework and aims at equitable access to energy, clean air and water, food, health and livelihoods and economic growth. The study connects elements of SD in an integrated bottom-up approach to understand the implications for economy, energy trajectories, emissions and costs. Any reduction of CO2 is treated as a co-benefit of the framework mentioned above.
Manufactured Sand Potential and Status in Karnataka
Sand is an essential element in concrete and hence plays an important role in the construction and infrastructure industry in a modern economy. It is typically sourced from riverbeds which are located in ecologically sensitive areas. Hence, excessive mining leads to the degradation of riverbeds, which affects the local groundwater system, potential biodiversity and the recreational potential of these regions. A large quantity of the official sand production per year in Karnataka is currently sourced from riverbed mining, some of which is also imported from neighbouring states.
Implementation of SAPCC: A Green Growth Approach
There are continuing concerns over economic and environmental developments in many countries - some of these have intensified due to prolonged global energy, food and financial crises. In this context, “green economy” was proposed as a means for catalysing renewed national policy development and international cooperation and support for sustainable development. However, there is still a lack of clarity around what “green economy policy” encompasses and how it integrates with national and sub-national priorities and objectives relating to economic growth and poverty eradication.
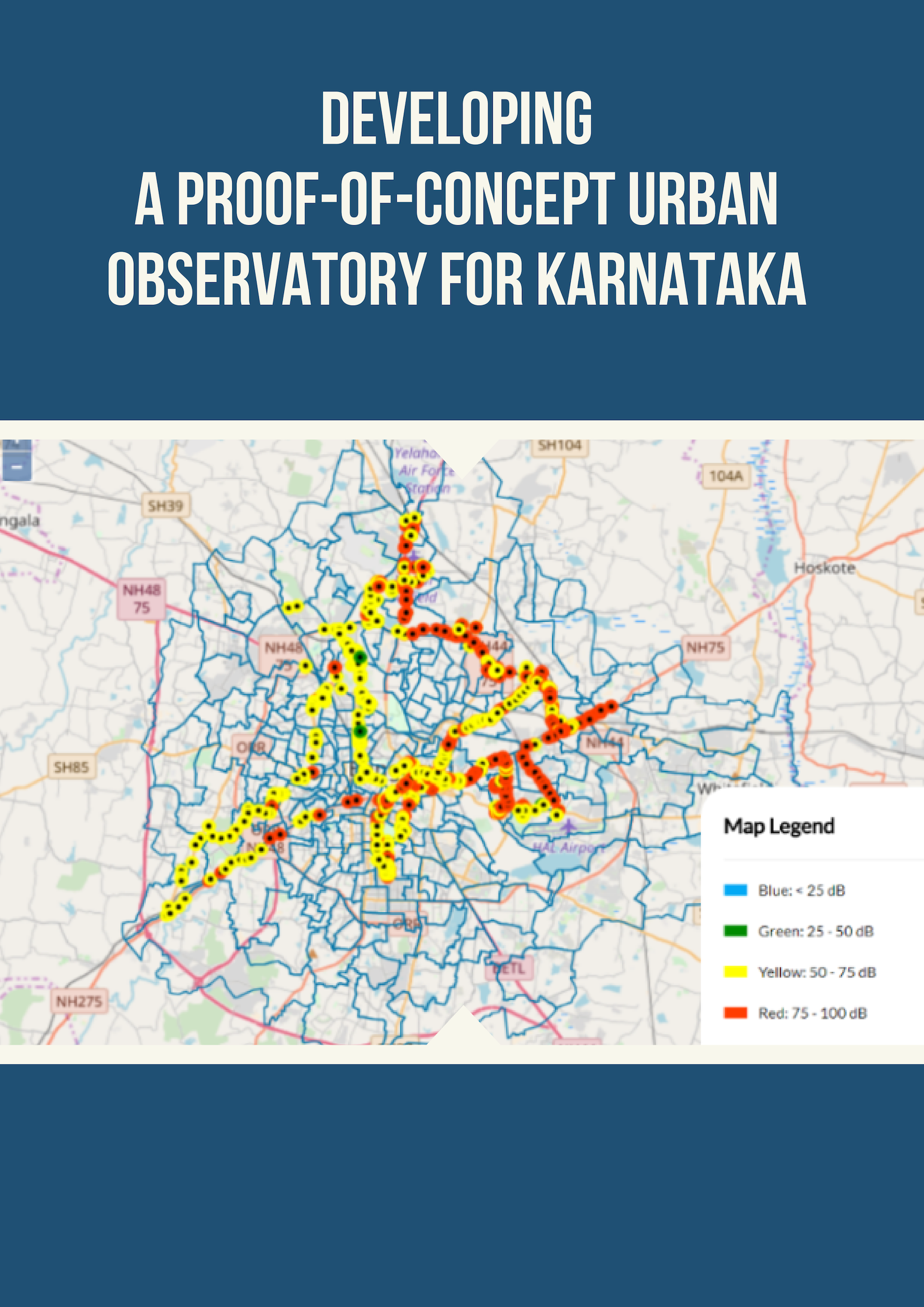
Sustainable urbanization using high speed rail (HSR) in Karnataka, India
Sustainable urbanization using high speed rail (HSR) in Karnataka, India.
Institutional analysis of urban transportation in Bangalore
Institutional analysis of urban transportation in Bangalore.This paper maps and explains the institutional structure of urban transportation policy in Bangalore, India. Our critique of individual agencies and methods of policy making and implementation will demonstrate how the current setup negatively affects urban transportation planning in Bangalore. We suggest about broad institutional changes that we believe would improve outcomes and service delivery.
